

About Skin Cancer
India experiences more than a million skin cancer cases a year. East and north India are highly susceptible to the disease due to arsenic exposure along the Ganges basin.
Skin cancer, prominent among males, is an abnormal growth of cells in the outermost layer of the skin. The mutations are triggered in the epidermis through damaged DNA.
Mutations cause the rapid multiplication of skin cells and the development of cancerous tumors.
Sun-exposed parts of the skin develop skin cancer (scalp, lips, face, neck, ears, arms, hands, and legs). Sometimes, skin cancer is also found in palms, toenails, fingernails, and genital areas.
Melanoma skin cancer can affect darker complexions and less exposed skin areas too. Skin cancer can happen to all skin tones irrespective of age, race, gender, climate, etc.


Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
- Advanced age and exposure to UV rays
- UV rays come from tanning beds, sun, sunlamps, etc
- Green or blue eyes and red or blond hair
- A light and natural skin tone
- Familial background and personal history of skin cancer or melanoma cancer
- Skin tones that can redden easily, burns, freckles
- Multiple moles
How can it be prevented?
- Protect skin from direct exposure to UV rays
- A minimum application of artificial sources of UV rays like sun lamps, tanning beds, etc
- Avoid indoor tanning procedure
Practice the following steps for a UV index of 3 or higher:
- Full-sleeve clothes that cover legs and arms
- Keep yourself in the shade
- Sunglasses and hats to protect against UVA and UVB rays
- Use sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher
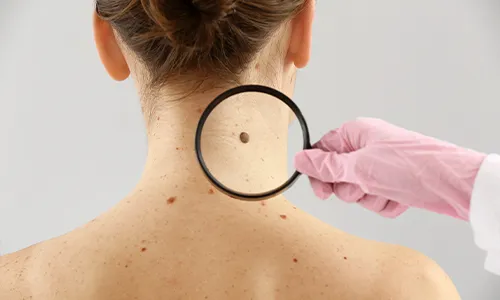

Screening and Diagnosis of Early-Stage Skin Cancer
- Screening of skin cancer includes self-evaluation and a clinical test.
- Healthcare provider checks moles, pigmented portions, and birthmarks on the skin. They look for size, colour, texture, and shape abnormalities. However, screening does not decrease the seriousness of the disease.
- Doctors recommend regular checks for skin cancer patients to observe any changes. You can also self-exam and report to the doctor for any worrisome developments.
- After screening and diagnosis of skin cancer, the doctor conducts a biopsy. The medical practitioner will extract suspicious tissues from the skin using a local excision.
- A pathologist analyses the extracted tissues to check whether it is benign or malignant melanoma. Patients can also try a second opinion.
- Melanoma develops on the epidermis, the outer layer of the skin and gradually grows deeper into the dermis (interior parts of the skin). The process is slow; therefore, it is easier to cure skin cancer if found before it grows.
- Melanoma is visible to the naked eye as it grows on the outer layer of the skin.
Doctors decide the type and stage of the skin cancer to begin treatment protocol after screening and diagnosis.


Mobile Applications for Early-Stage Skin Cancer Detection
- UMSkinCheck: A free app developed at the University of Michigan
- MoleMapper: Developed at Oregon Health & Science University
- Miiskin
- MoleScope
- And others
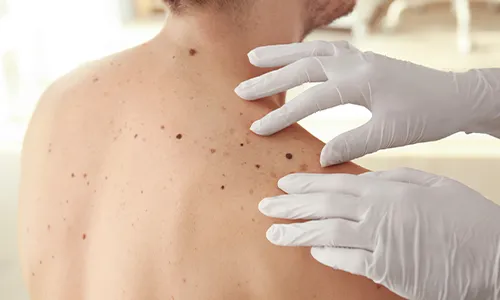

Types of Skin Cancer and their Symptoms
There are two main types of skin cancers : Non-melanoma skin cancer and Melanoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma and Squamous cell carcinoma are two main types of melanoma skin cancer.
Basal cell cancer targets the neck or face.
Its symptoms are:
- A flesh or brown-coloured flat scar looks like a lesion
- A waxy or pearly cancer lump under the skin
- A scabbing or bleeding sore that keeps coming
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
People with dark skin often develop squamous cell skin cancer on unexposed skin areas. The disease generally affects the ears, hands, and face.
Symptoms are a flat lesion with a crusted and scaly skin surface and a reddish firm nodule.
Melanoma Cancer
Melanoma skin cancer can grow anywhere in the human body, and Melanoma also develops through an existing cancerous mole.
Usually, it affects the trunk and face in males and lower legs in females. Melanoma cancer can also spread to covered parts of the body.
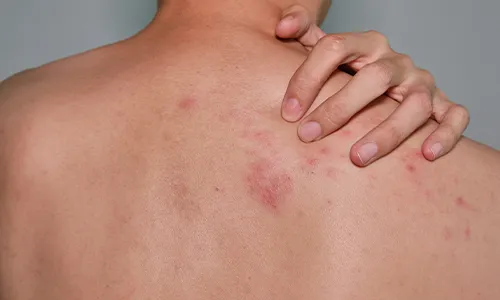

Signs of Melanoma Skin Cancer
- Asymmetry – One half can look different the other half.
- Border – It can have a jagged or uneven edge.
- Color – It can have different colors or a mix of colors (like brown, black, and red).
- Diameter – It is larger than the eraser on the end of a pencil.
- Evolution – Its size, color, or shape can change over time.
Symptoms :
- Itchy and painful lesions.
- Dark speckles and large brownish spots.
- A mole that changes size, colour, and feels.
- Red, white, blue or black coloured lesions with irregular portions and border.
- Dark lesions on soles, fingertips, toes, mucous membranes, and palms.
Signs and symptoms vary as per different melanoma stages. The doctor will confirm staging after detailed screening and diagnosis.


Rare or Less Common Skin Cancers
- Kaposi Sarcoma develops in people with weak immune systems due to medication or other conditions. It grows in blood vessels in the skin and causes purple or red patches.
- Sebaceous Gland Carcinoma is aggressive and rare skin cancer. It grows in the oil glands and is often mistaken as an eyelids problem.
- Merkel Cell Carcinoma grows in the neck, trunk, and head. Cancer develops beneath hair follicles and skin.
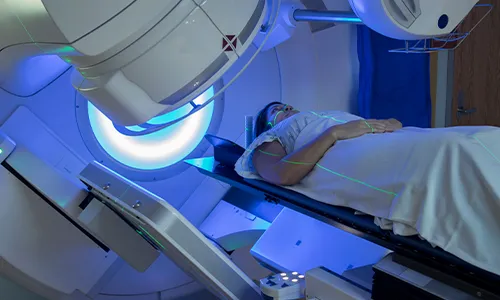

Modalities for Staging and Treatment
Post-diagnosis, doctors conduct the following tests and procedures for staging:
- CT Scan
- Chest X-Ray
- PET Scan
- Ultrasound Scan
- Eye Exam with Diluted Pupil
- Lymph Node Biopsy
The standard procedure of skin cancer treatment includes:
- Surgery (including Mohs Surgery)
- Radiation Therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Photodynamic Therapy
- Chemical Peel
- Targeted Therapy
- Immunotherapy


Follow-up Appointments and Cancer Care
- Consult your doctor for a follow-up appointment schedule during the maintenance phase of the cancer treatment.
- Keep an eye on any symptoms of recurrence and report to the doctor if found.


FAQs
-
What is the most common type of skin cancer?
Basal and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common forms of skin cancer.
-
Why are males diagnosed with skin cancer more than females?
Men are more exposed to direct sun during various activities, making them more susceptible to skin cancers.
-
What is the most dangerous type of skin cancer?
Melanoma is the most aggressive and deadly type of skin cancer.
-
What is metastasized skin cancer?
Metastasized skin cancer means the spread of malignant melanoma or other skin cancer types beyond the primary point of growth.
-
Can skin cancer be inherited?
Around five to ten per cent of melanoma skin cancer cases are hereditary. It usually happens due to an altercation in genetics or some pathogenic gene variant.
Specialized Doctors at M | O | C
Find the nearest center
Cancer Centres
Mumbai
Pune
Rest of Maharashtra
Gujarat
Delhi NCR
Cancer Clinics
Borivali
+91 9920767626
Book Your Appointment



























.png)









.png)




















.png)
.png)
.png)



